When we started doing our first PT qualifications we noticed that the course materials and resources we were given weren’t particularly good and that there was a lack of good online resources to help people studying to become PTs. Having qualified and also spent time teaching PT courses, we decided to remedy that.
Therefore, this is a resource for anyone studying to become a personal trainer (or teaching people who are) but even if you just want to know more about the science behind what you do in the gym then you should still find it useful.
The main sections on this part of the site are:
Level 2 Certificate in Gym Instructing: covering many topics in the first course you’ll do when qualifying as a PT.
Level 3 Diploma in Personal Training (Practitoner): looking at many topics from the second course you’ll do in order to fully qualify as a PT.
Supplementary Topics: useful resources for areas not properly covered on these courses but useful for a PT to know.
Level 2 Certificate in Gym Instructing
Whilst these articles do not cover the full syllabus for this course, they nonetheless include a lot of diagrams, tables and methods of explaining things that should usefully supplement the main course materials.
Furthermore, the revision sheet at the bottom contains pretty much all the key points that you’ll need to know, and there’s then a mock exam so you can test yourself.
These articles are grouped together under the relevant topic heading as they usually appear in the Level 2 Anatomy manuals:
The Structure and Function of the Circulatory System
The Chambers of the Heart including the atria, ventricles and major blood vessels.

The Structure and Function of the Respiratory System
The Journey Taken by Air as it is Inhaled including the bronchi, bronchioles and alveoli.

The Structure and Function of the Skeleton
The Five Main Functions of the Skeleton such as support, protection and storage.
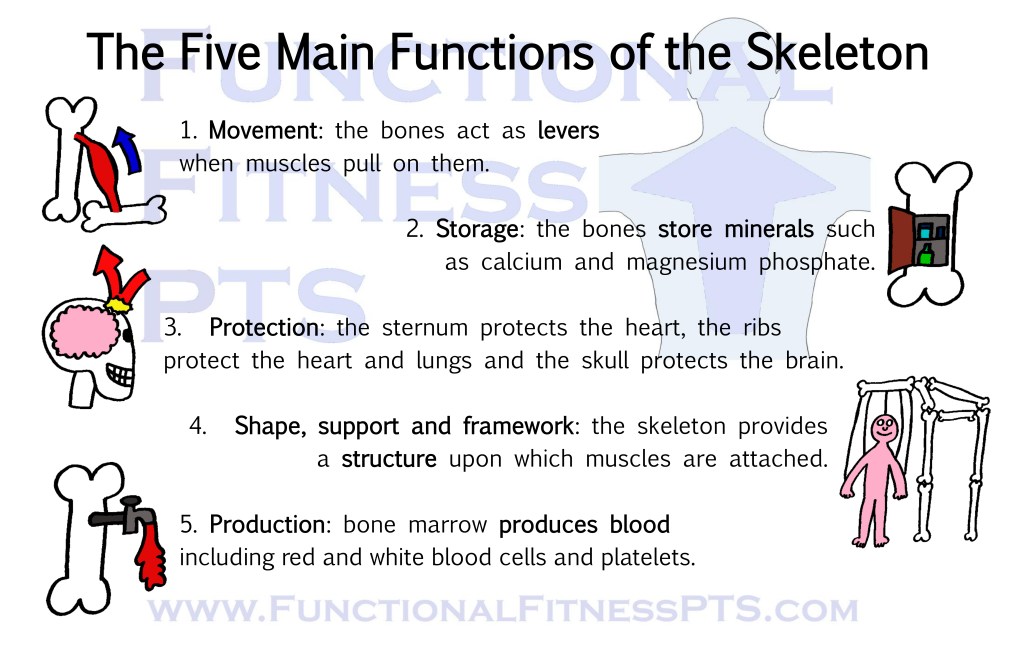
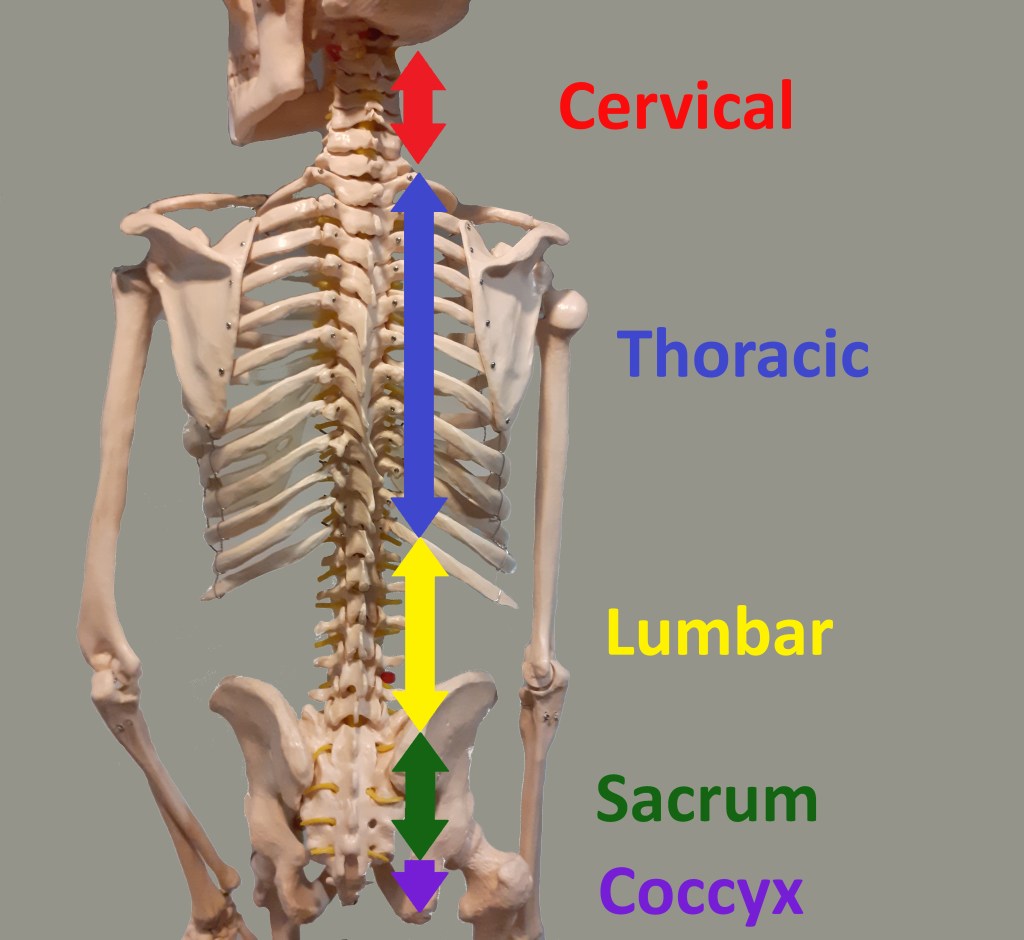
The Five Sections of the Spine: the cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacrum and coccyx.
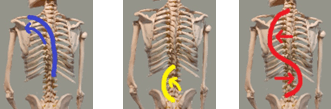
The Three Main Postural Deviations: kyphosis, lordosis and scoliosis.
The Joints of the Skeleton
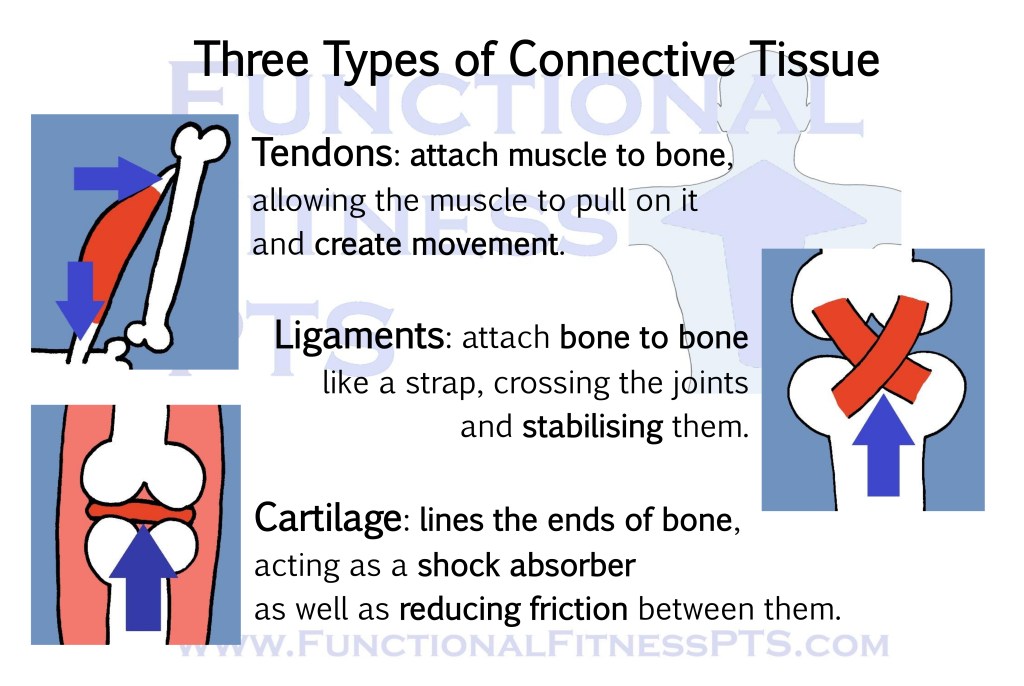
Three Types of Connective Tissue: tendons, ligaments and cartilage.
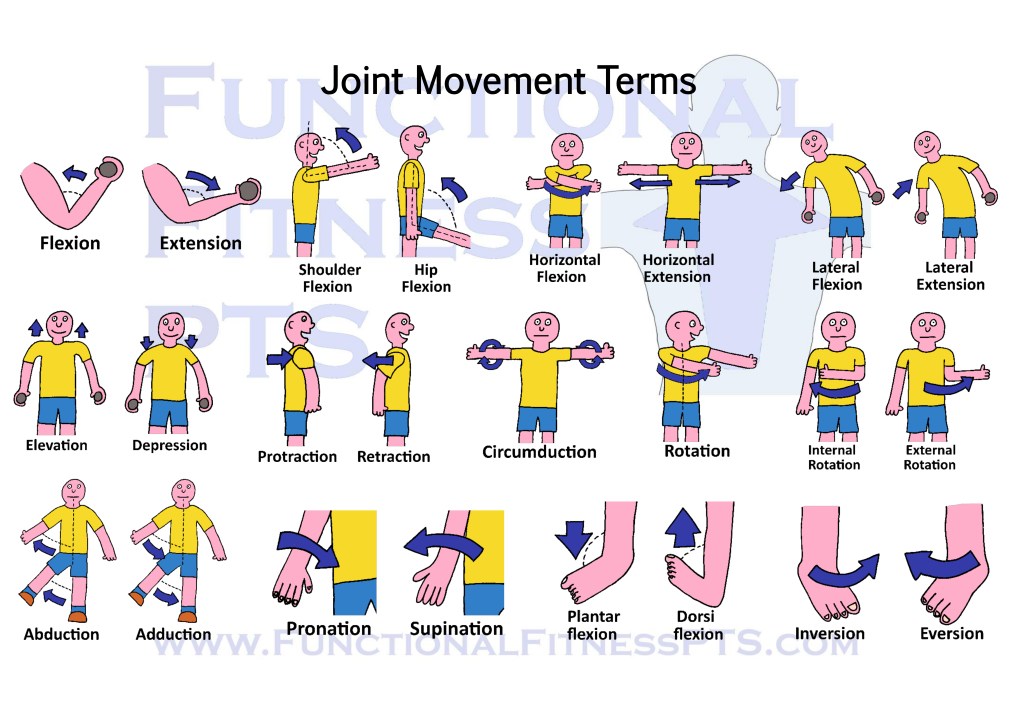
Joint Movement Terms: just what do all those terms like flexion, extension, pronation and supination mean?
The Muscular System
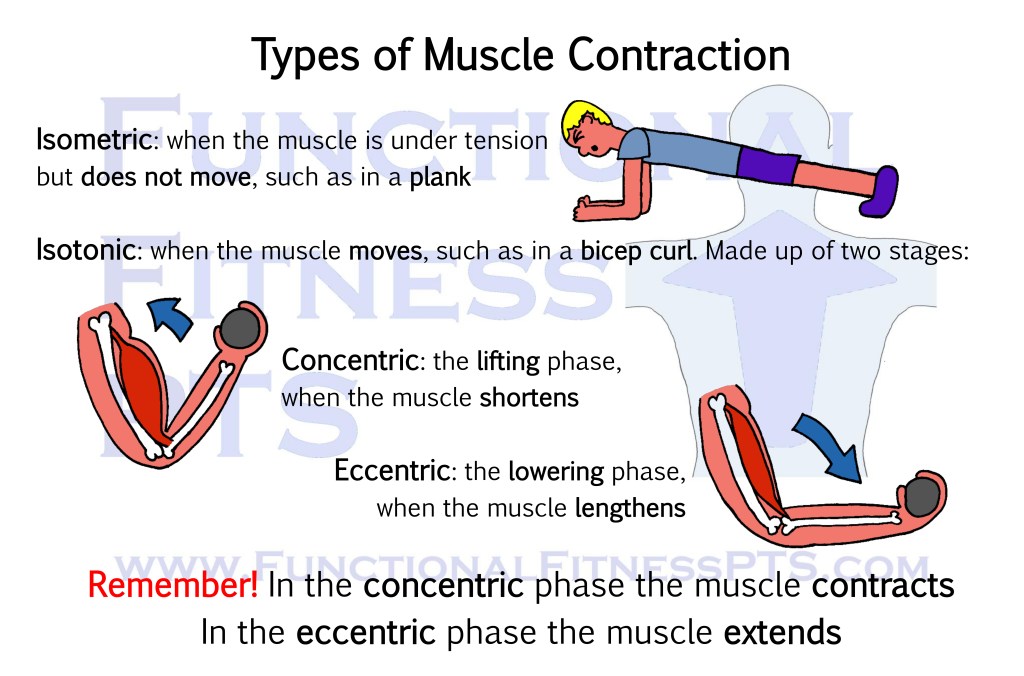
The Types of Muscle Contraction: isometric and isotonic, including concentric and eccentric.
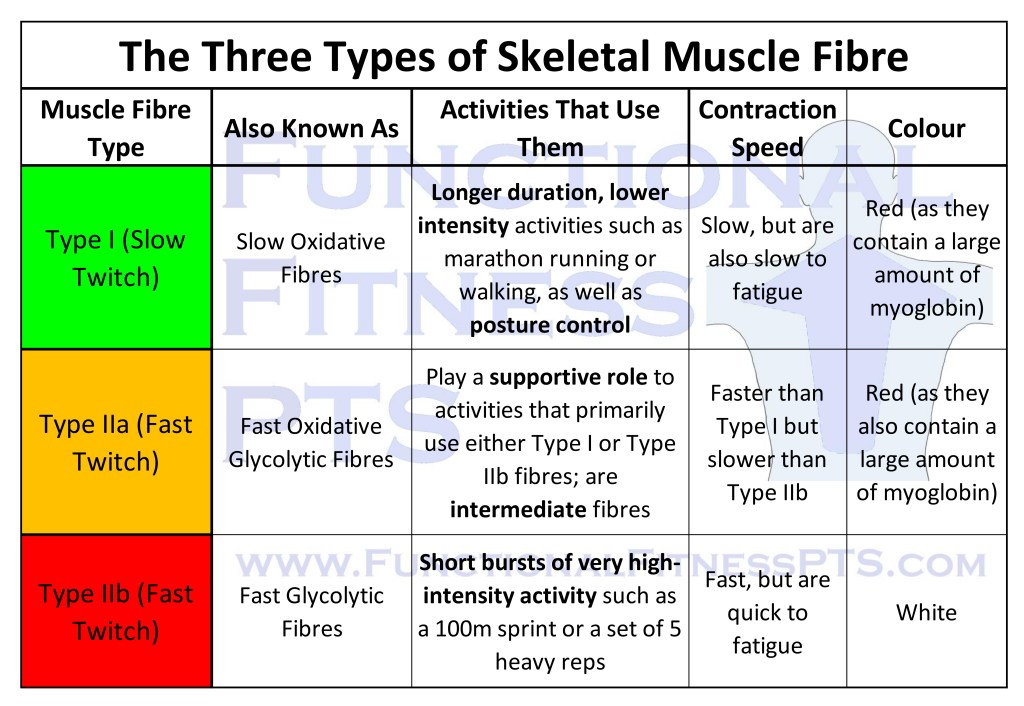
The Three Types of Skeletal Muscle Fibre: Type I, Type IIa and Type IIb
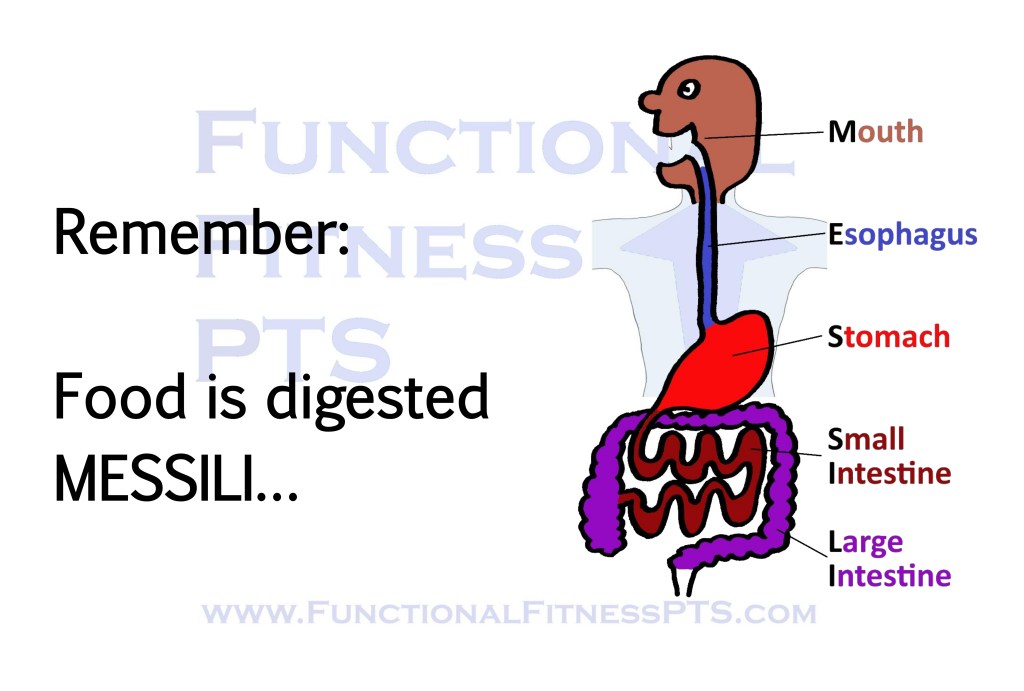
The Structure and Function of the Digestive System
The Journey Taken by Food During the Digestive Process
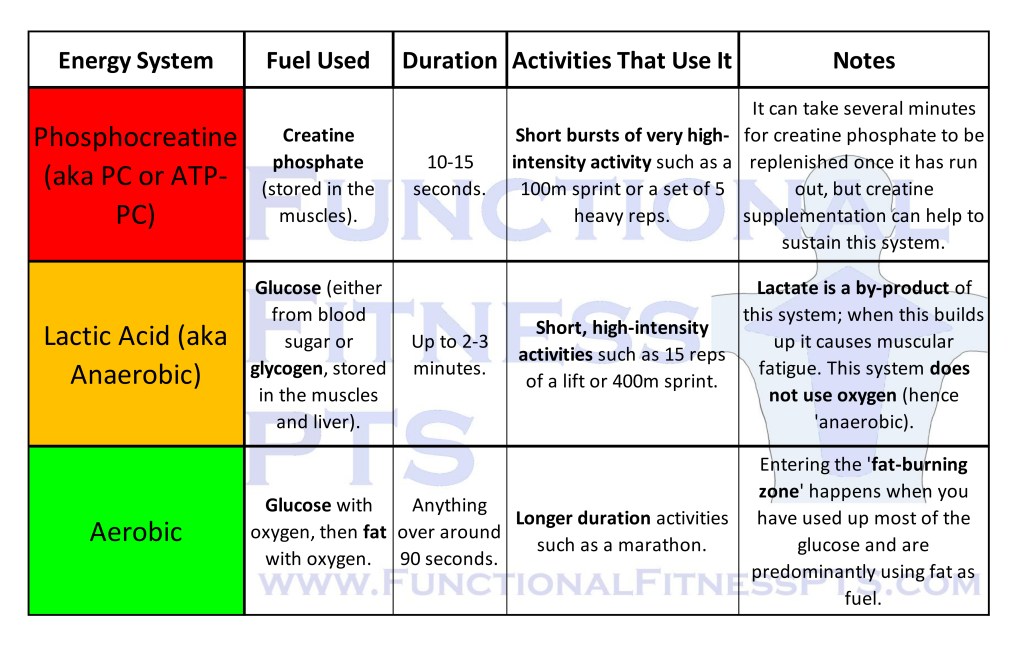
Energy Systems and Their Relation to Exercise
The Three Energy Systems: phosphocreatine, anaerobic/lactic acid and aerobic.
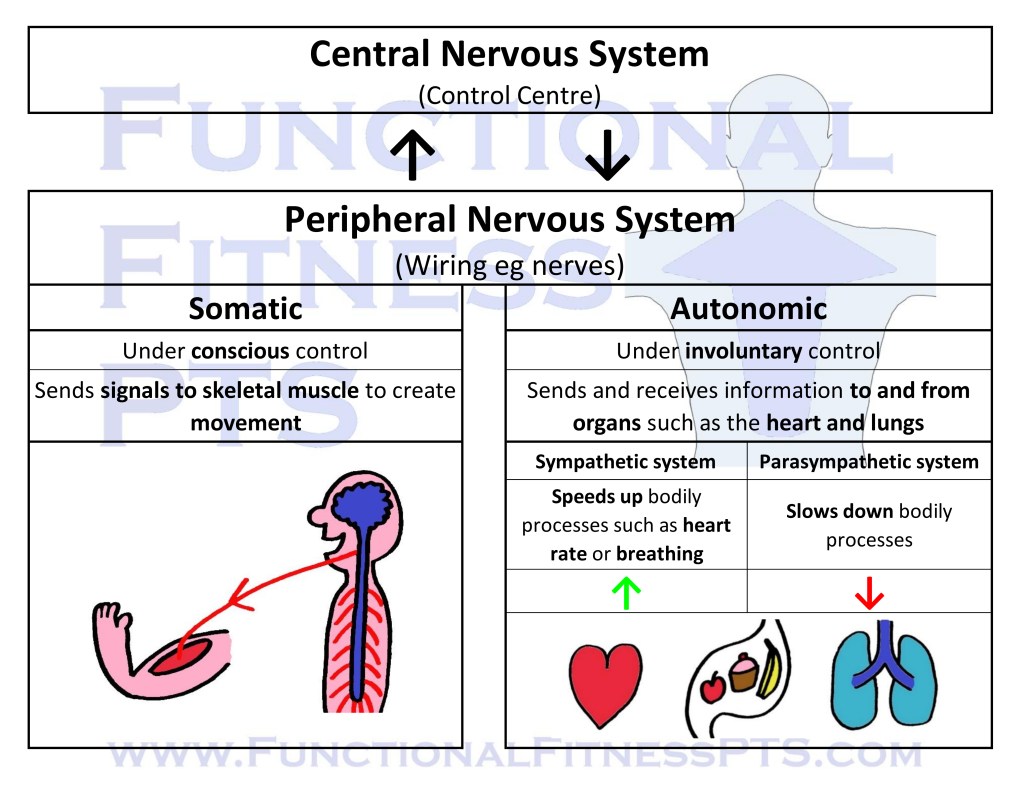
The Nervous System
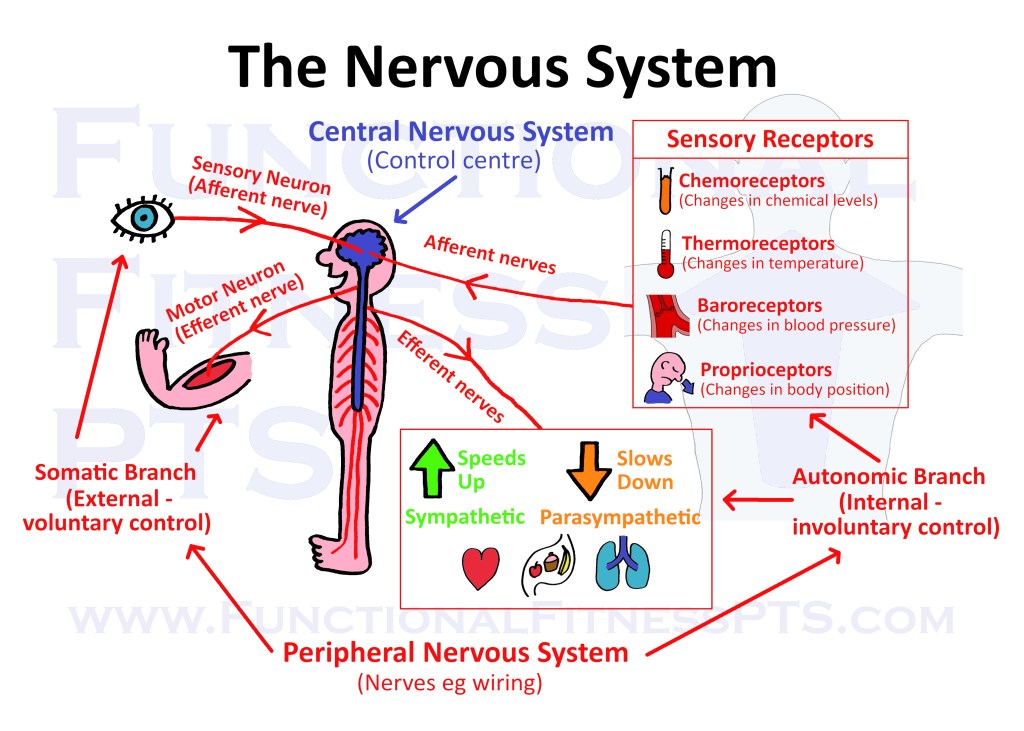
The Nervous System including the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system.
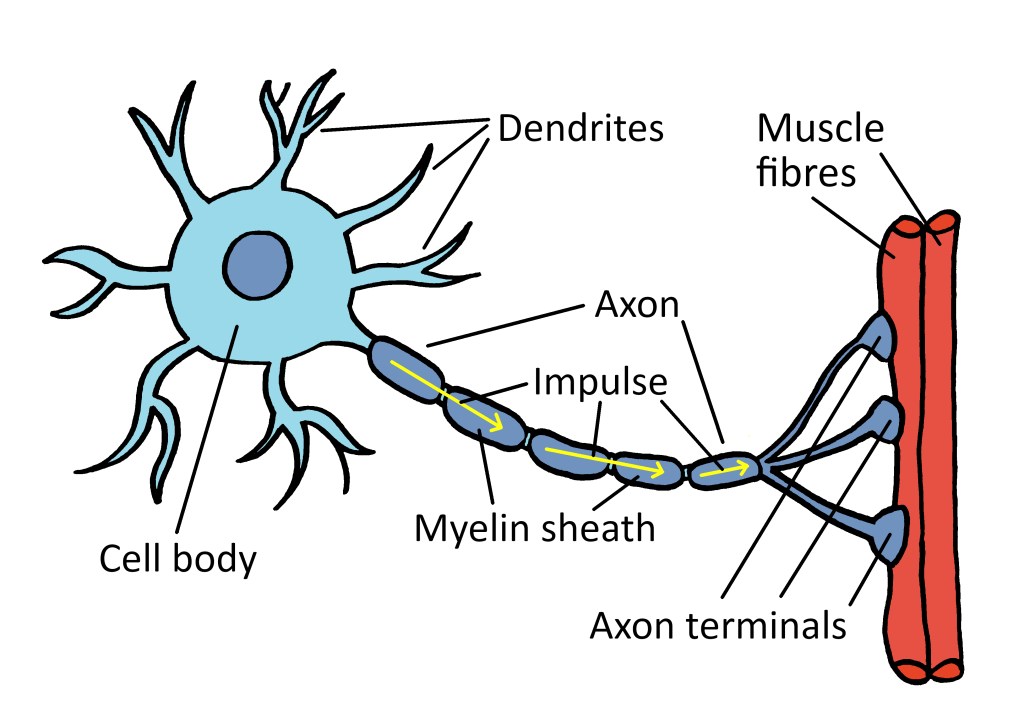
What is a Neuron? A look at the structure and function of a neuron.
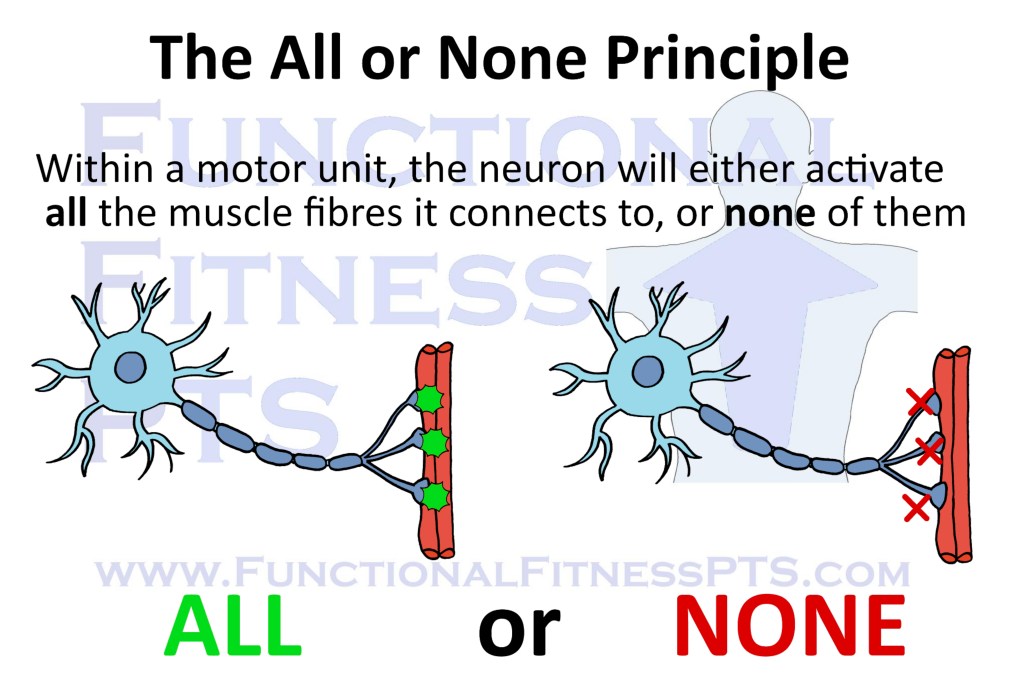
The All or None Principle: a rule about neurons that the exam always wants you to know.
Level 2 Revision Sheet and Multiple Choice Mock Exam
Once you’ve gone through the whole anatomy syllabus, check out this revision sheet, which covers most of the main points of the unit:
And if you’re feeling confident, here’s a mock exam for the Level 2 PT qualification. It covers all the topics, and the questions are the kind of thing you’ll find in the actual exam, along with a few others to encourage you to think:
Other Syllabus Topics
These articles relate to selected topics from the other course units that may be useful:
A Guide to Mobility, Warming Up, Cooling Down and Stretching: explaining the different types of stretching, as well a pulse-raising and pulse-lowering, and where to place all this within a workout.

Micronutrients, as covered in the unit Lifestyle management and health awareness.

Nutrition, covering a wide range of topics including the structure and function of protein, calorie calculation, BMR, some common nutrition questions and other topics relevant to this unit.

The Borg Scale: a common system used to measure exercise intensity.

Level 3 Diploma in Personal Training (Practitioner)
Again, we haven’t covered the whole syllabus here (hey, it’s a long, complicated and involved course so that’s your tutor’s responsibility!) but what we have included is some useful ways of remembering things that may well be in the exam.
The Level 3 topics currently covered are:
The Nervous System including the new things added at Level 3: four types of sensory receptor as well as afferent and efferent nerves.
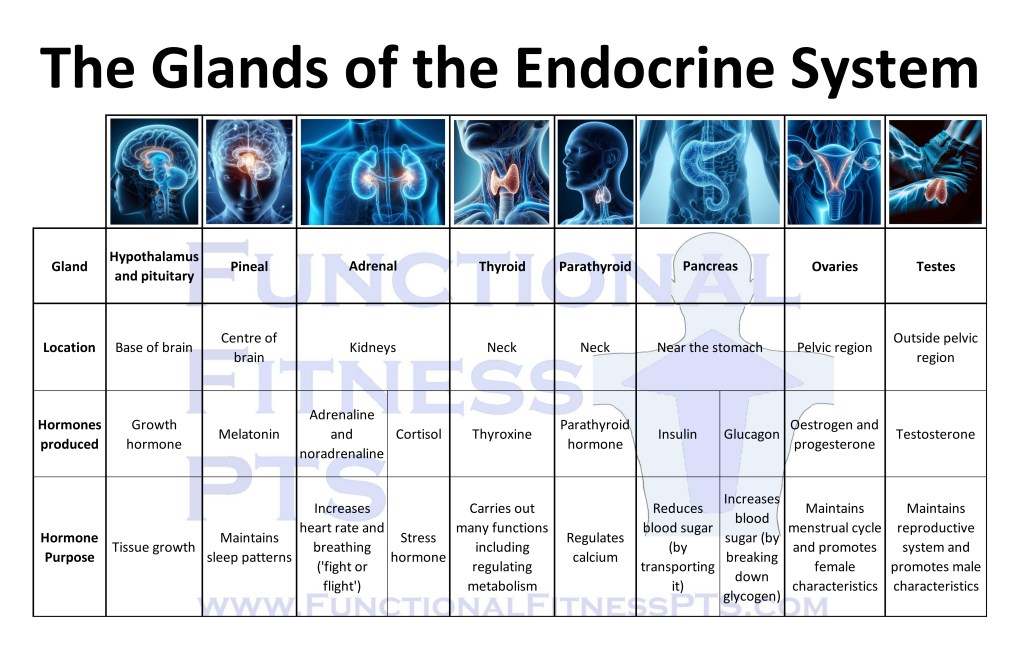
The Endocrine System, which sends signals around the body using chemical messengers called hormones.
The Three Types of Skeletal Muscle Fibre: Type I, Type IIa and Type IIb, but with the new details introduced at Level 3 such as contraction speed and alternative names.

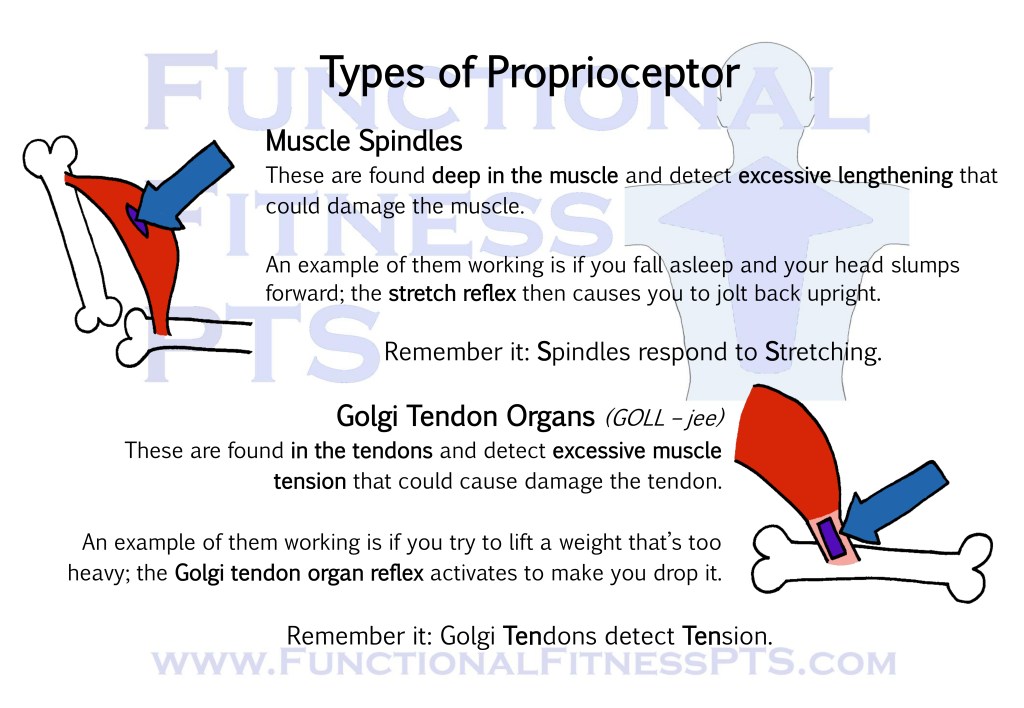
Muscle Spindles and Golgi Tendon Organs: a look at the difference between these two types of proprioceptor.
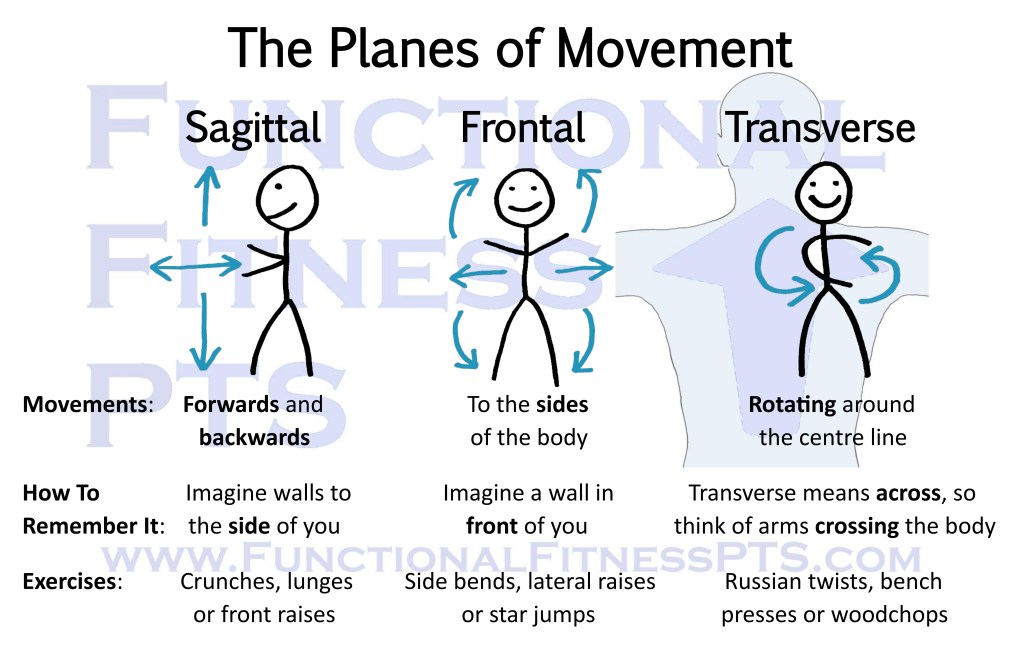
The Anatomical Planes of Movement: frontal, sagittal and transverse, and how to remember the difference.
The Three Classes of Lever: the three types of lever found in the body.

Arteriosclerosis vs Atherosclerosis: the differences between these two conditions affecting the arteries.

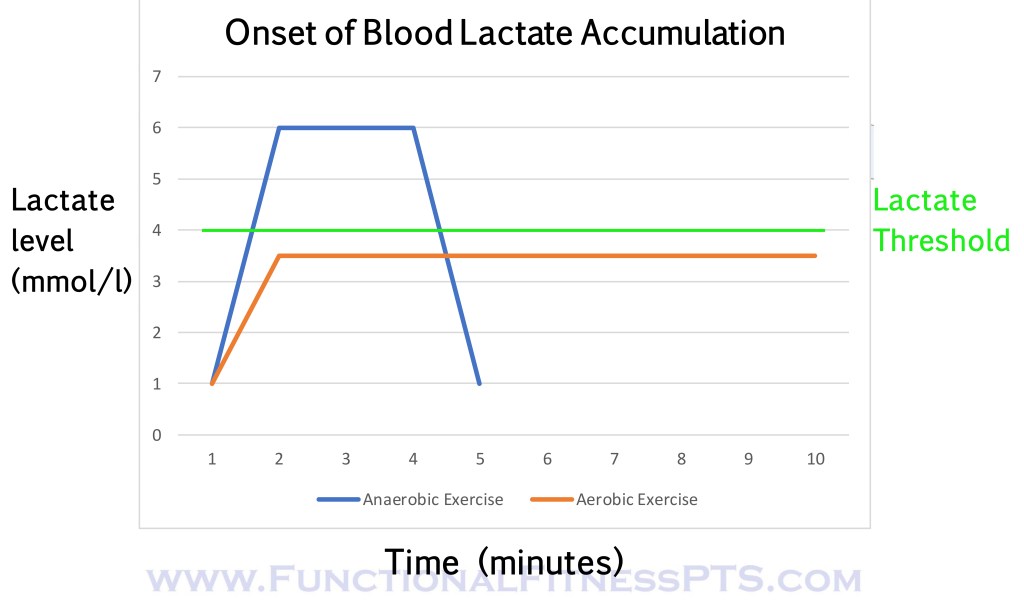
Onset of Blood Lactate Accumulation, or OBLA, including the difference between this and DOMS.
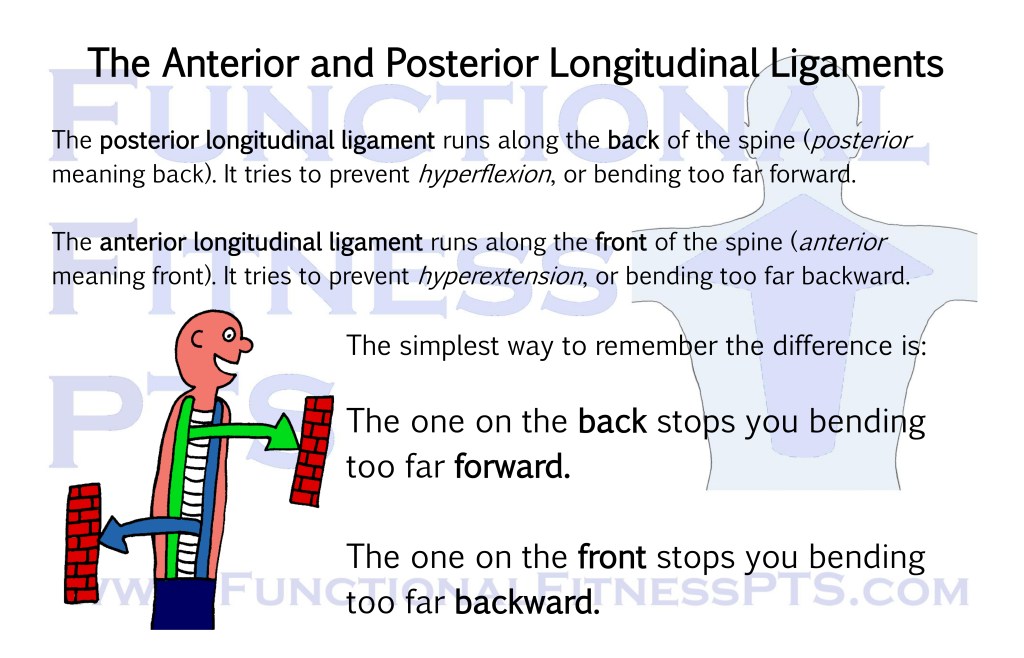
The Anterior and Posterior Longitudinal Ligaments: two ligaments that prevent excessive bending of the spine.
Micronutrients: the different vitamins and minerals covered in the unit Nutrition to support physical activity.

Nutrition: articles relevant to this unit, including some common questions and some links to help you calculate a client’s nutritional needs.
Level 3 Anatomy Revision Sheet and Mock Exam
Here’s a revision sheet for the anatomy unit exam, too. It doesn’t cover everything, but should help you remember the key points of the syllabus:
And here’s a mock exam for the anatomy unit of the Level 3 personal trainer course:
Supplementary Topics
There are a number of subjects that aren’t properly covered in the Level 2 and Level 3 syllabuses but are still useful for a personal trainer to know, so we’ve put together some articles looking at them. At present, they cover:
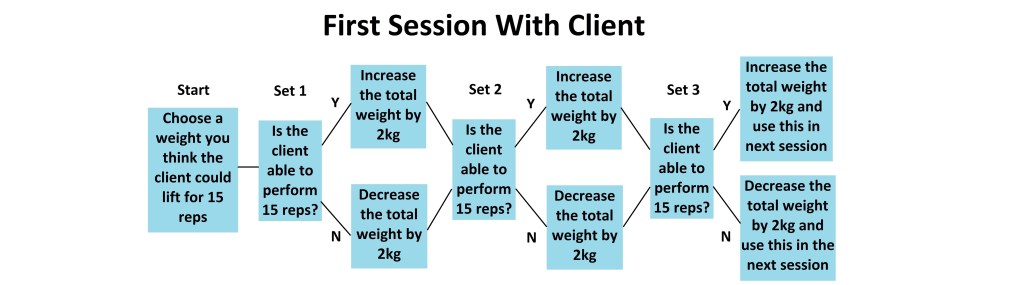
How Can I Find Out What Weights I Should Use With New Clients?, an article explaining a way of establishing a client’s abilities before improving them.
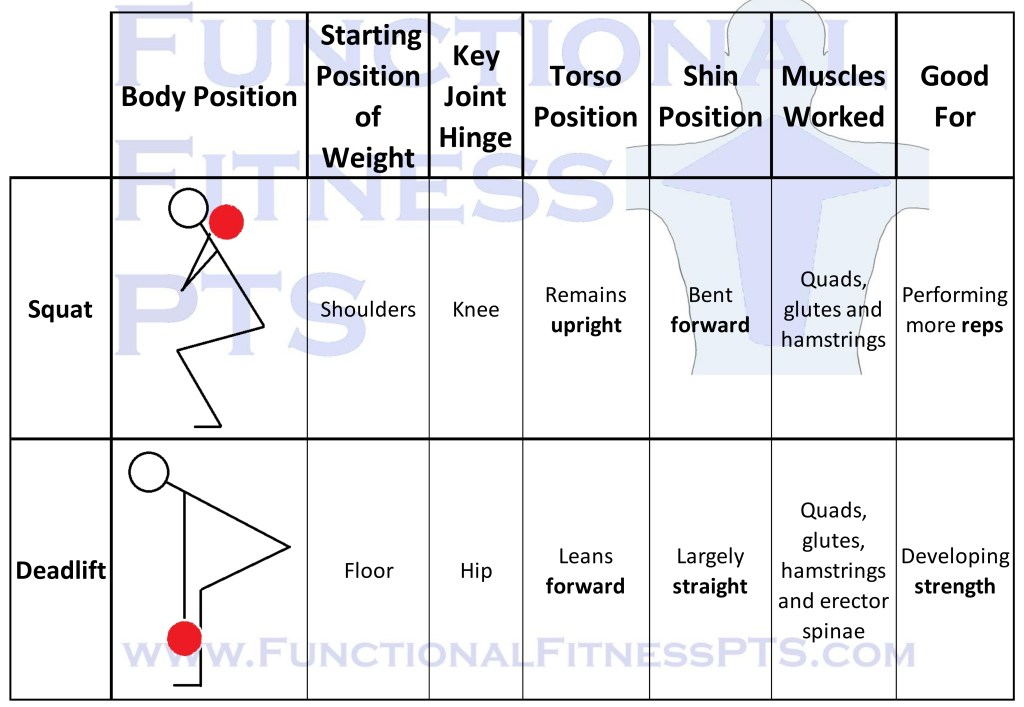
The Differences Between a Squat and a Deadlift, so you can advise clients on correct form and technique.
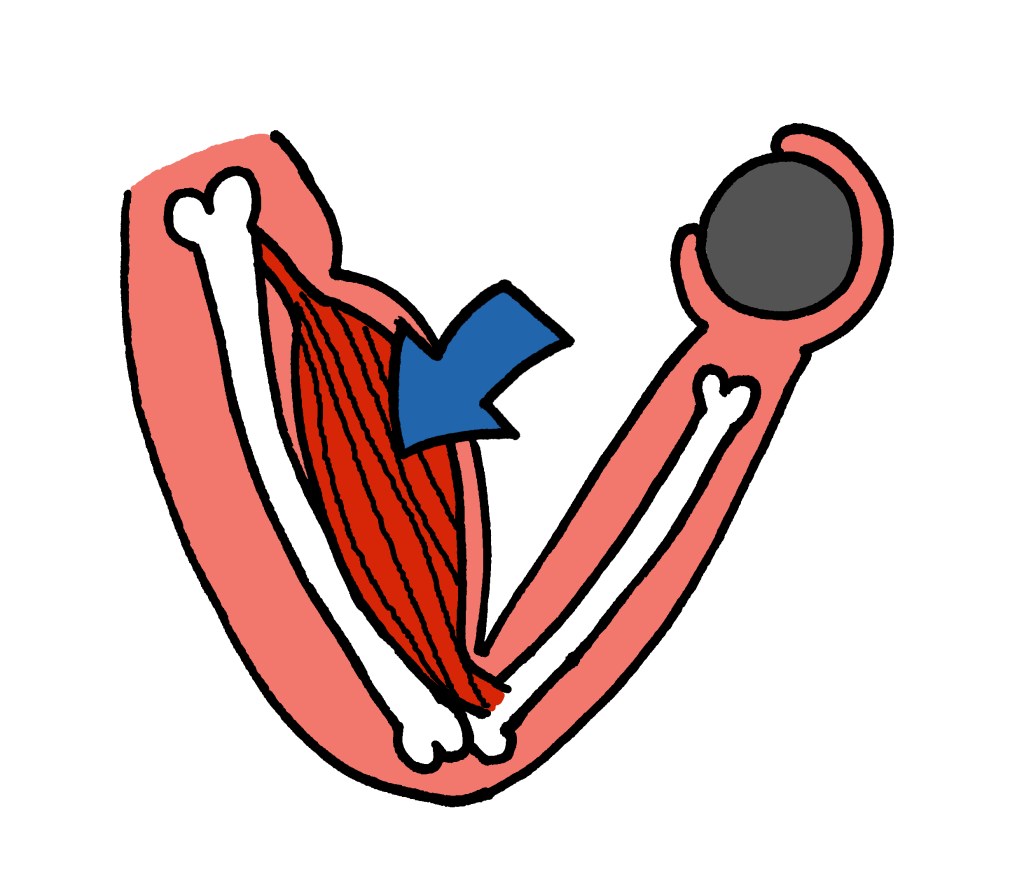
What is Hypertrophy?: hypertrophy refers to making muscles bigger, but how does it work?
Protein, Amino Acids and BCAAs: a look at the functions of protein, its structure and recommended intake.

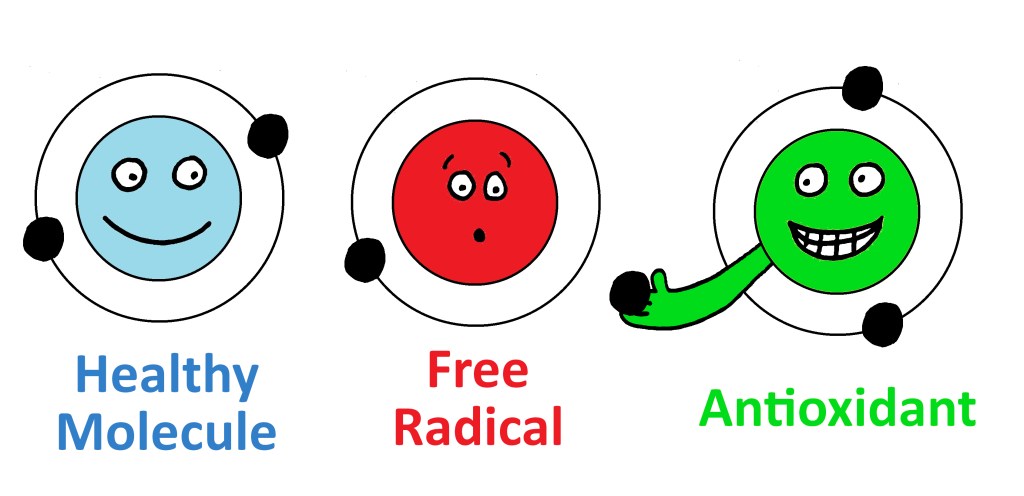
Free Radicals and Antioxidants: what these things are and what they do.